
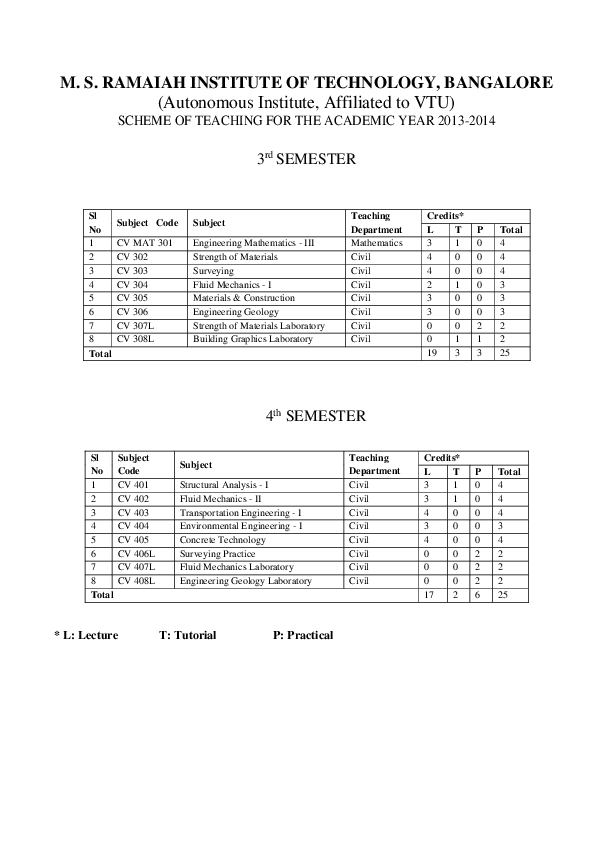
in other position, the switch SD connects the galvanometer to the unknown e.m.f and. to be measured, can be connected in the galvanometer circuit. the circuit diagram of cropton potentiometer is: In the above a galvanometer G is connected in series with a switch S1 and a double throw SD, by means of which either the stander cell E2 or the e.m.f. Standard A.C and D.C potentiometer, Principle and standardization and application. two variable resistors, R1 consisting of a number of coils for coarse adjustment and R2 in the form of a slide-wire fine adjustment of the potentiometer current, are used in series with a battery E1 of 2 volts. The basic principle of the potentiometer is that the potential drop across any section of the wire will be directly. there are two slide contacts C1 and C2 : C1 sliding over the slide-wire AB and C2 sliding over the studs of the resistance coils PA. the slide-wire is connected in series with 14 resistance coils PA, each of which has a resistance exactly equal to that of the slide wire.
it consists of a graduated slide-wire AB having resistance usually of the order of 10 ohms. Construction: The circuit diagram of a Crompton d.c. The effect of a very long slide-wire is achieved by connecting a number of resistance coils in series with a comparatively short slide-wire.

This is the modified version of the slide-wire potentiometer where in calibrated dial resistors with a small circular wire of one or more turns are used thereby reducing the size of the instrument. Its accuracy depends on uniformity of the wire. Crompton Potentiometer: the slide-wire potentiometer discussed earlier is very limited use of this.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
